Research
Rapid digitization and increased dependency on communication systems has transformed the energy sector. This transformation is accompanied by several threats and challenges. Therefore, our research is centered on the existing and upcoming challenges of the evolving energy sector. We mainly focus on cybersecurity, operational resiliency of cyber-physical systems, optimization and control of smart energy networks, in particular on the application of power electronics in the control of clean energy resources e.g. solar, wind, tidal, and wave energy resources.
Cybersecurity
Zoom and Pan Instructions: • Scroll to zoom • Click and drag to move • Pinch and drag on touchscreen devices
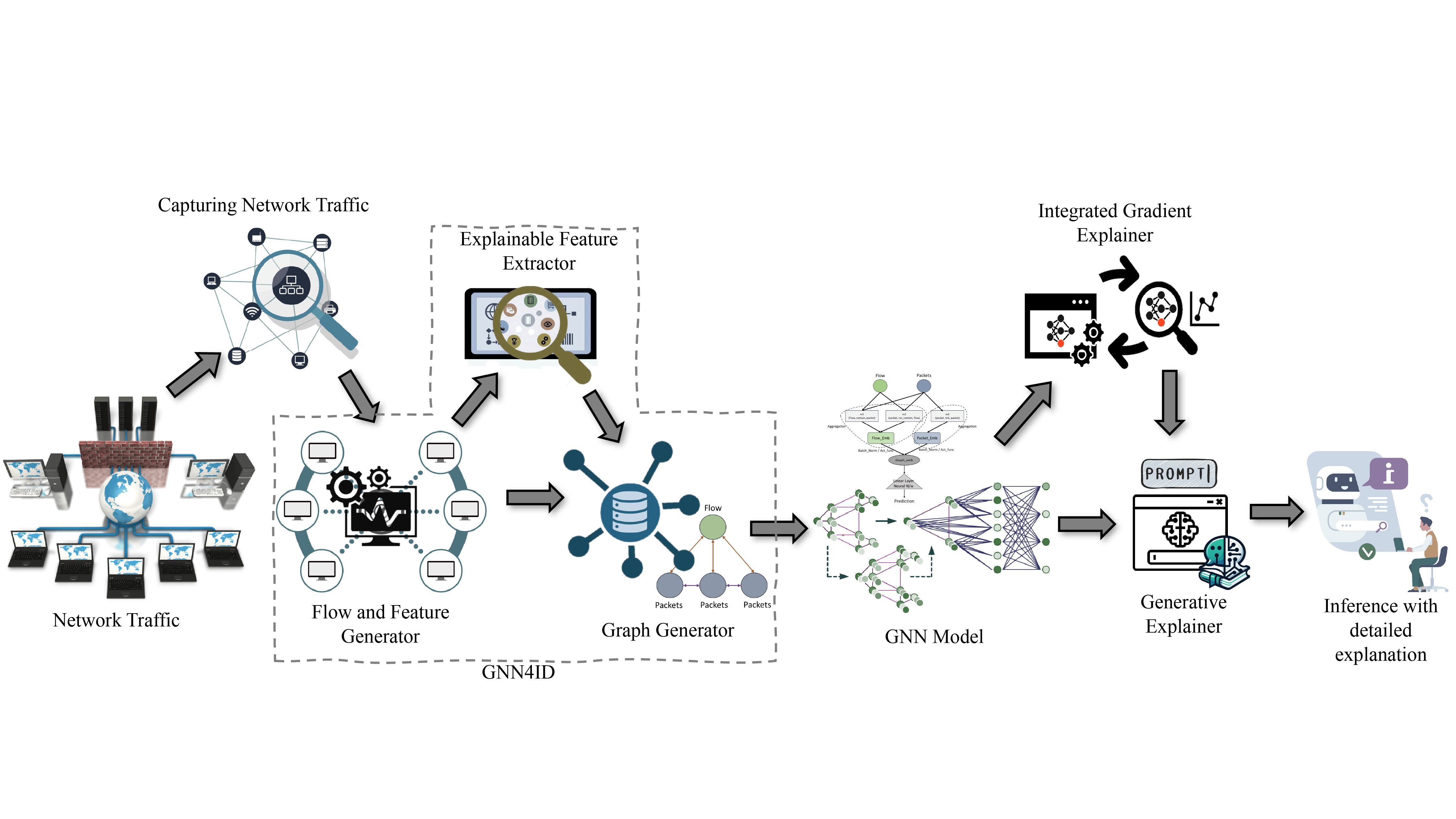
Cyberspace operations encompass military missions, intelligence activities, industrial control systems, IoT ecosystems, and critical infrastructure environments operating in and through cyberspace. These operations require resilient, adaptive, and intelligence-driven cyber capabilities that generate defensive and strategic effects across interconnected digital and cyber-physical domains. As adversaries increasingly employ stealth, obfuscation, and AI-evasive techniques, cyber defense must evolve beyond static detection mechanisms toward semantically aware, explainable, and autonomous systems. Secure cyberspace operations therefore demand trustworthy AI architectures capable of operating effectively in contested and rapidly evolving threat environments.
Therefore, to support this vision of secure cyberspace operations, the research group focuses on the following areas:
- Development of explainable and adversarially robust intrusion detection systems for military, IoT, and industrial environments.
- Design of reinforcement learning–based autonomous response and intrusion prevention systems for adaptive threat mitigation.
- Integration of semantically aware, multi-modal machine learning and large language models to fuse heterogeneous data sources and enhance contextual threat detection and cyber-physical defense.
Selected Publications (2025):
- Wali, S., Farrukh, Y. A., & Khan, I. (2025). Explainable AI and random forest–based reliable intrusion detection system. Computers & Security.
- Khan, I., Wali, S., & Farrukh, Y. A. (2025). RADIANT: Reactive autoencoder defense for industrial adversarial network threats. Computers & Security.
- Wali, S., Khan, M. I., & Imran, M. (2025). Semantic-aware reinforcement and ensemble learning for signal management and anomaly detection in IoT systems. Scientific Reports.
- Wali, S., Farrukh, Y. A., & Khan, I. (2025). Semantic-aware web security: Detecting attacks with a large language model.
- Wali, S., Farrukh, Y. A., & Khan, I. (2025). Covert penetrations: Analyzing and defending SCADA systems from stealth and hijacking attacks.
Smart Grid System Resiliency
The Smart Grid System Resiliency area focuses on enhancing the robustness and adaptability of modern power systems through the integration of cutting-edge technologies. Our research explores the use of machine learning (ML) and explainable AI (XAI) to improve the predictability and transparency of grid operations, ensuring that smart grids can efficiently respond to dynamic challenges. We are particularly interested in the development of digital twins for smart grids, which allow for real-time monitoring and simulation of grid behavior, thereby enhancing decision-making and system optimization. Security and resiliency are central to our work, as we investigate distributed optimization techniques to bolster the stability of microgrids and protect against cyber threats. Through these efforts, we aim to create a more resilient, secure, and efficient power infrastructure capable of withstanding and adapting to unforeseen disruptions.
Key Areas of Interest:
- Integration of machine learning (ML) for predictive analytics and optimization in smart grid systems.
- Application of explainable AI (XAI) to enhance transparency and trust in grid operations.
- Development of digital twins for real-time monitoring and simulation of smart grid behavior.
- Enhancing the security and resiliency of smart grids against cyber threats and physical disruptions.
- Distributed optimization techniques for improving the stability and efficiency of microgrids.
- Advancing the robustness of power infrastructure to ensure reliable and adaptable energy distribution.
Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation is at the forefront of revolutionizing various operations across industries by integrating advanced machine learning techniques. By leveraging machine learning, we are able to optimize and automate processes, making them more efficient, reliable, and adaptive to changing conditions. One of the key aspects of our research is the application of computer vision, which enables machines to interpret and respond to visual data in real-time, leading to significant improvements in quality control, predictive maintenance, and operational safety. Furthermore, we are deeply invested in exploring the realm of explainable AI (XAI) to ensure that the decisions made by automated systems are transparent, understandable, and trustworthy, thereby enhancing their adoption and effectiveness in critical applications.
Key Areas of Interest:
- Application of machine learning to optimize and automate industrial processes.
- Enhancing process efficiency and reliability through intelligent systems.
- Integration of computer vision for real-time visual data interpretation and response.
- Development of predictive maintenance models to reduce downtime and improve safety.
- Exploration and implementation of explainable AI (XAI) to ensure transparency and trust in automated decisions.
- Advancing the reliability of automated systems in dynamic and uncertain environments.
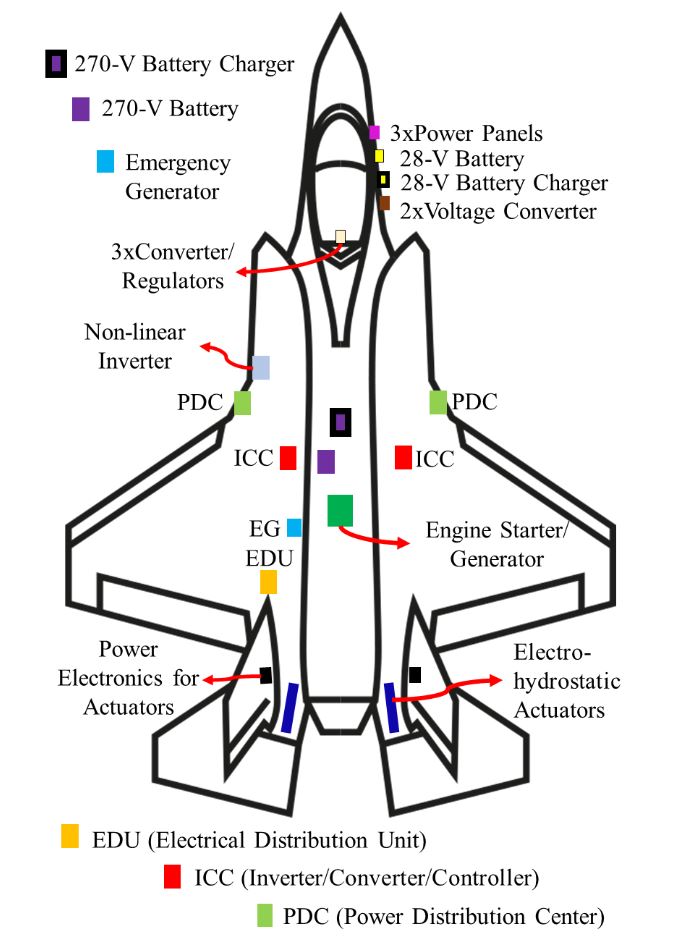
Electrical Power System of Military Aircraft F-35 [1]
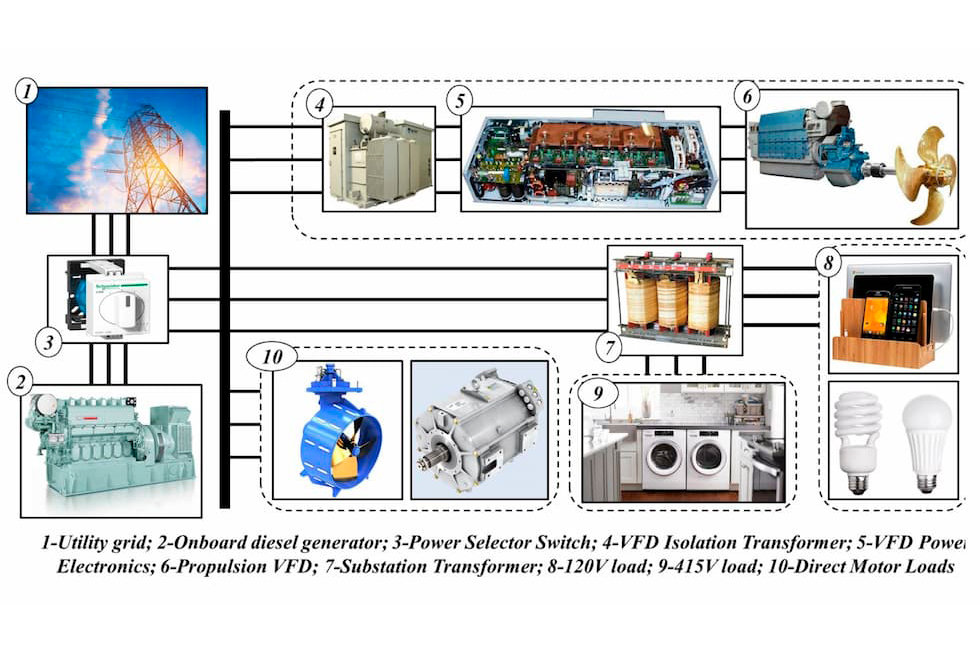
Cold-Ironing solution to minimize greenhouse emissions from onboard diesel generators [2]
Design and operation of custom-built microgrids for powering land and marine transportation systems are currently undergoing rapid changes to become clean-energy compliant. To achieve this, innovative solutions to incorporate clean energy sources (concentrated as well as distributed) are under development. Another field of interest is to alter the conventional electrical power system to minimize weight, improve efficiency, and facilitate easy integration of renewable energy sources. Typical examples include renewable energy integration in aircrafts, distributed propulsion systems, alternate energy fed marine shipboards, and cold-ironed marine vessels.
The team at CARES lab is currently working on different innovative solutions to meet these evolving demands. An interesting field of work is the development of "Integrated Power Electronics Building Blocks (iPEBB)", wide-band gap realized converters operating at high switching frequencies (thereby minimizing size, increasing power density, and higher efficiency). In these iPEBB blocks, the control software defines the hardware capabilities. Through this iPEBB, novel concepts such as distributed filtering and distributed energy storage solutions are being explored. Another interesting area of work is to investigate novel electrical power system architecture through the state-of-the-art solid state transformers. These solutions help in fast response to circuit anomalies, and improve power quality.
The major topic of interests includes (but not limited to):
- Solid-state transformer based electrical power system to facilitate cold-ironing in marine vessels.
- Distributed filtering solution to address power quality concerns in marine vessels.
- Modeling and investigation of transient loading on electrical power system of military aircraft.
- Distributed energy storage solutions to address pulse load and transient capability requirements of next-generation military aircrafts.
- Design and development of unmanned aircraft vehicles (UAV) with high power density and engine starting capabilities.
References:
- Irfan Khan, Syed Rahman, “Detailed Modeling and Investigation of Impact of Transient Loading on Electrical Power System of Military Aircraft F – 35”, In IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo, pp. 1-6. IEEE, 2022.
- Rahman, Syed, and Irfan A. Khan. "Investigation of Power Quality Issues in Cold Ironed (Shore Connected) Grid Connected Electric Ships." In 2020 54th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, pp. 1353-1358. IEEE, 2020.
Power Electronics & EV Systems
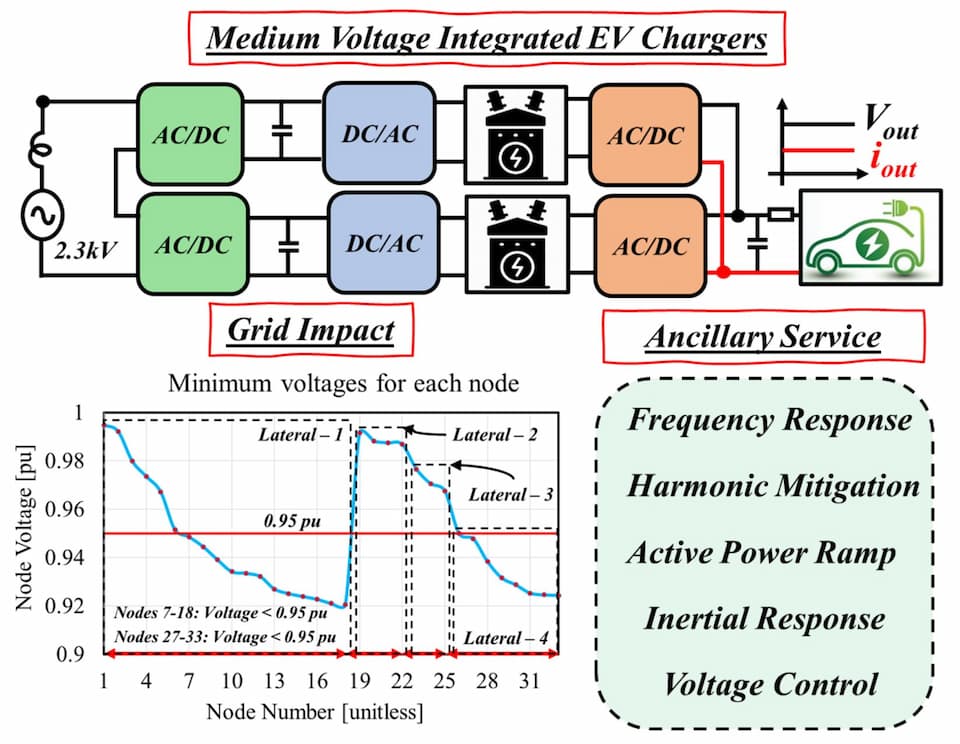
Development of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of realizing transportation electrification. Innovative and efficient slow/fast/superfast chargers are now available commercially and are being deployed to support the EV adaptation. Adding these charging loads to the utility grid will have its impact and must be analyzed to address the performance concerns as well as realize the underlying potential opportunities. The research team at CARES lab is analyzing the impact of adding different EV charging loads to the low-voltage distribution system using historical data of two geographically different locations. This approach helps in identifying the impact of system parameters' and the impact on the development and installation of charging stations. Additionally, using distributed generators for improving the grid performance is also under investigation.
Another area of interest for the team is the opportunity to control the cumulative EV batteries through Vehicle-to-Grid mode. Operation in this mode enables the ancillary services, required for improving stability and performance of the utility grid. The ancillary services include peak shaving, voltage/frequency regulation, economic benefits to both consumers and supplier, and optimal power quality.
The major topic of interests includes (but not limited to):
- Development of innovative and efficient fast/superfast charging solutions.
- Analysis of slow/fast/superfast charging load on the performance of low-voltage distribution grids.
- Renewable energy based innovative solutions to maximize EV penetration in distribution grids.
- Direct integration of fast/superfast charging stations to the medium voltage lines.
- Utilization of EV fleet as a potential source to provide ancillary services to the grid and minimize deployment of additional battery storage solutions.
If you are looking to collaborate with our lab or are interested in being a student, we would like to hear from you. Our lab is always looking for good opportunities, be they business deals or an excellent student for our lab.